Web Portal vs Website: 7 Essential Differences to Understand
06 December
In the current world of information technology people have different means to interact, share information and do business online. Two of the most frequently used terms today are ‘web portal’ and ‘website.’ Although they look very similar it is possible to identify the difference in the given couple of options because they have different functions and are aimed to meet different needs of users. If you’re unsure about the difference between the two or considering which is right for your goals, this article will break down seven key differences between a Web Portal vs Website.
What is a Website?
A website is defined as a group of interconnected web pages that commonly share the same domain name. It is designed to convey a message, sell a service, or even create an interface for a person to interact with a business or person. Websites can be viewed by anyone with a connection to the internet and are usually used as the fixed or at least relatively stable presence on the world wide web. 94% of first impressions are design-related, and users tend to spend 88% more time on a website with audio-visual elements.
What is a Web Portal?
A web portal, in contrast, is an individualized access to diverse Web site resources, applications and information relevant to the individual using the portal. They typically must be signed into and are developed to provide a specific and user specific interface, or a dashboard, application or database. Examples are web applications supporting online banking, securely accessing an organization’s internal network known as intranet and web application for accessing student information in schools or colleges. according to statista, almost 59 percent of global web traffic in the second quarter of 2022 was via mobile devices.
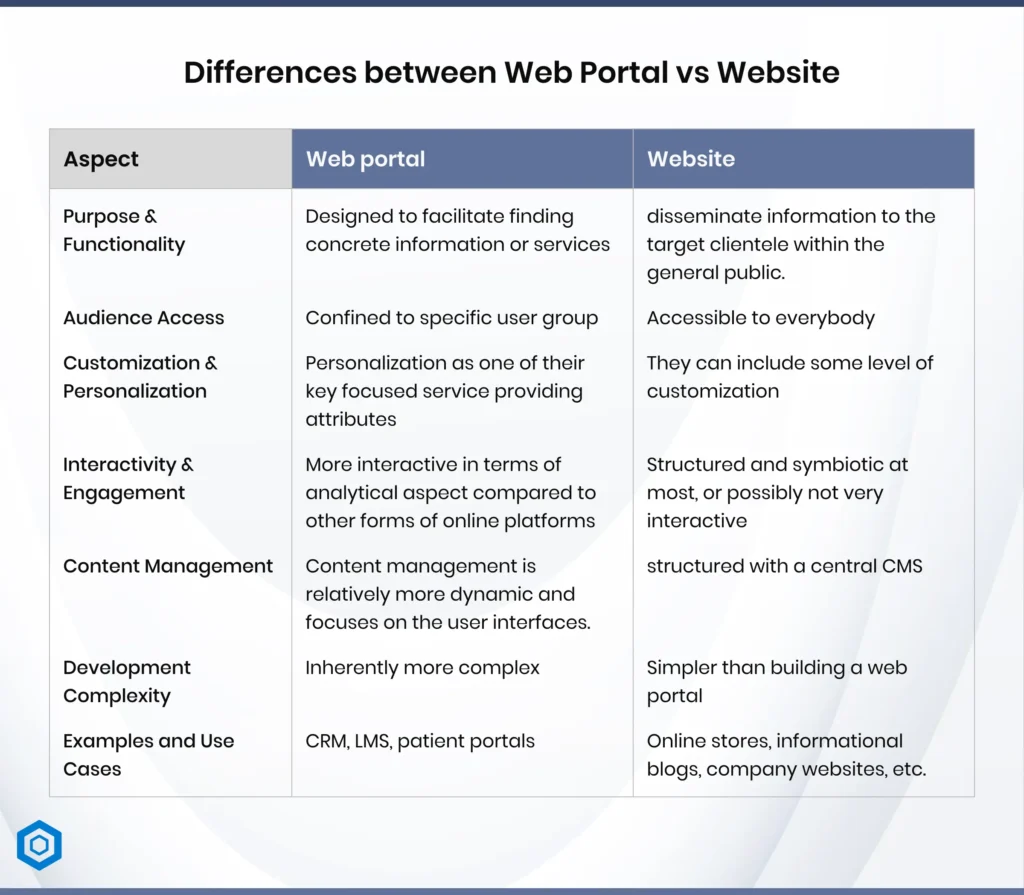
Differences between Web Portal vs Website.
- Purpose and Functionality
This difference is in the basic concept of the documents. A website’s chief purpose is to disseminate information to the target clientele within the general public. This information could be such as a promotional message, an educational piece or simply a commercial one. Web sites are nearly always of a general character and have a general public as their populace.Web portals, however, are special purpose tools designed to facilitate finding concrete information or services. They are more engaging and the content is targeted. For instance, a healthcare portal may provide an ability to set an appointment, review health records or use a messaging system to contact a doctor.
- Audience Access
Websites are generally accessible to everybody and any person can access the information regardless of logging in or not. They are intended for maximum usage and can not be easily protected or need a login to access.On the other hand, web portals are designed to involve user identification. They are confined to specific user group, for example, the organizational worker, consumers, or learners. Such login allows the content to be specific to the user’s requirements.
Ready to build your Android app?
Contact us - Customization and Personalization
Web portals are designed with personalization as one of their key focused service providing attributes. After a user logs in their profiles, information presented to them is according to their personalized options, positions, or authorities. For instance, an employee using terminal that connects to his or her company’s intranet receives his or her timetable, to-do list, and department-specific messages.Websites, while they can include some level of customization (like language selection or region-based content), are not typically built for highly personalized experiences. Most users see the same information when they visit a website.
- Interactivity and Engagement
Web sites are commonly structured and symbiotic at most, or possibly not very interactive. Even if today’s website might contain forms, chatbots, or even e-commerce capabilities, their purpose is the dissemination of information and not complex user interactions.Web portals are more interactive in terms of analytical aspect compared to other forms of online platforms such as Websites and Blogs. These solutions are typically equipped with templates like dashboards, forums, message boards, or other active tools by which users can interact with the system actively as well as physical and digital resources. This makes portals suitable for activities such as accounting, making of application or working on a project.
- Content Management
Most websites are structured with a central Content Management System (CMS) through which the site’s administrators can create, edit and publish content. The aim is in maintaining continuity and presentability of the site for all users or visitors.In web portals, content management is relatively more dynamic and focuses on the user interfaces. While administrators still control the structure of the application and its interface, the information the user encounters is dynamic. For instance, web app development company for news might share global headlines to one user, sharing regional news to another user depending on their choice or geographic location.
Want to reduce Android app development costs?
Contact Us - Development Complexity
Creating a website is often simpler than building a web portal. Websites typically rely on straightforward frameworks or CMS platforms like WordPress, Squarespace, or Joomla. The website development process focuses on design, responsiveness, and content structure.Web portals are inherently more complex, requiring advanced development frameworks and technologies. They must integrate multiple systems, databases, and applications to deliver a seamless user experience. Security is also a bigger concern due to the need for user authentication and data protection.
Examples and Use Cases
The distinction becomes clearer when examining real-world examples.
Websites:
Examples include online stores like Amazon, informational blogs, company websites, and news outlets such as CNN. These platforms are built for general access and are primarily designed to inform or sell.Web Portals:
Examples include employee portals, customer relationship management (CRM) portals, online learning management systems (LMS), and patient portals. These platforms are tailored to specific users, offering tools and resources to accomplish tasks for wordpress website development.Bring your Android app idea to life!
Check our portfolio.
How to Decide Between a Web Portal and a Website
When deciding whether to build a Web Portal vs Website, it’s essential to identify your goals and audience.
Choose a website if your primary aim is to share information, promote products or services, or attract a broad audience. Websites are versatile and cost-effective for businesses and individuals looking to establish an online presence.
Opt for a web portal if you need to provide users with personalized content, tools, or services. Portals are ideal for businesses or institutions that require secure access to specific resources, like educational platforms or internal corporate systems.
Conclusion
While both Web Portal vs Website serve valuable purposes in the digital landscape, understanding their differences is critical to leveraging their capabilities effectively. A website is perfect for sharing information with a broad audience, while a web portal is your go-to solution for personalized, secure, and interactive user experiences.
By analyzing your audience’s needs and your objectives, you can choose the right platform to achieve your digital goals. Whether you aim to engage the public or provide tailored services to a select group, knowing these differences ensures your online presence aligns with your strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, it is true that when the clients need to design the UI/UX individually, or need a special animation, it will cost more.
While integrating new features and enhanced capabilities, additional support, updates or compatibility issues with new versions of Android also increases the long-term costs.
Yes, the use of such technologies as AI, AR, or IoT will make the project more complex and will require tighter budgets and cost on development.
Yes you can consult with a team of developers to give you the accurate estimated price for your project specifications.