Image Processing Unleashed: Applications, Techniques, and Future Innovations
Written by: Gracy Christian | 15 DECEMBER
In contemporary technology, images have permeated every facet of our lives, and the significance of wonders of image processing has surged as an essential tool for extracting valuable data, enriching visual content, and facilitating myriad applications across diverse industries. This article seeks to unravel the fascinating domain of image processing, exploring its wide-ranging applications, advanced techniques, and the promising frontiers it unveils for the future – a journey into the wonders of Image Processing.
Understanding Images
Before delving into the wonders of image processing, it is essential to grasp the fundamental components of an image. An image is defined by its dimensions, which determine its height and width, typically measured in pixels. For instance, a 500 x 400 image contains 200,000 pixels.
Each pixel represents a point within the image with specific attributes such as color, shade, or opacity. There are different pixel representations:
Grayscale: In this representation, a pixel is expressed by a single integer ranging from 0 to 255. A value of 0 denotes complete black, while 255 represents full white.
- RGB: The RGB representation consists of three integers, each ranging from 0 to 255, representing the intensity of red, green, and blue. Combining these intensities produces a wide range of colours.
- RGBA: An extension of RGB, the RGBA representation includes an additional alpha field representing the image’s opacity. The alpha value determines the pixel’s transparency, facilitating the composition of multiple layers.
Image processing involves applying predefined operations to every pixel in an image, executed in a fixed order from the first operation to the last. These operations yield individual results for each pixel in the picture.
What Is Image Processing?
Image processing is a branch of signal processing that aims to enhance or extract essential information from an input image. It utilizes various techniques to modify the appearance or derive alternative image versions while preserving its meaningful features. As technology advances, image processing has become a pivotal area of research and study within computer science and engineering.

Applications of Image Processing
Image processing finds extensive applications across numerous domains, some of which include:
- Medical Imaging: Image processing techniques play a crucial role in medical imaging for tumour detection, segmentation, and image reconstruction tasks. This enables accurate diagnoses and precise treatment planning.
- Surveillance and Security: Image processing is vital in surveillance systems, enabling object detection, face recognition, and real-time tracking. It enhances security measures in public spaces and safeguards sensitive areas.
- Robotics and Autonomous Vehicles: Image processing allows robots and autonomous vehicles to perceive and interpret visual data, facilitating navigation, object recognition, and informed real-time decision-making.
- Remote Sensing: Image processing is crucial in analyzing satellite and aerial imagery for applications like land cover classification, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
- Entertainment and Gaming: Image processing techniques are widely used in the entertainment industry for special effects, character animation, and virtual reality, creating immersive visual experiences.
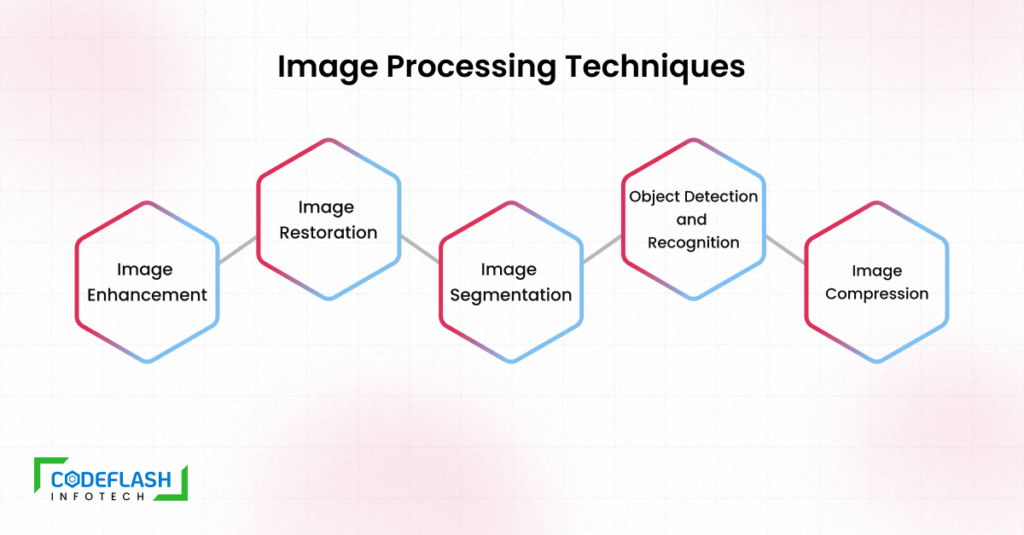
Image Processing Techniques
Image processing encompasses a wide range of techniques, each serving specific purposes. Some commonly used methods include:
- Image Enhancement: Techniques like contrast adjustment, noise reduction, and image sharpening are employed to improve the visual quality of images, making them more straightforward and informative.
- Image Restoration: This technique aims to restore degraded or damaged images caused by motion blur, noise, or compression artefacts, allowing for more precise visualization of essential details.
- Image Segmentation: Image segmentation involves partitioning images into meaningful regions or objects. It is employed in various applications such as object recognition, medical imaging, and video surveillance.
- Object Detection and Recognition: These techniques involve identifying and localizing specific objects or patterns within an image or a video stream, enabling applications like facial recognition, object tracking, and autonomous driving.
- Image Compression: Image compression techniques reduce the storage space required for images while minimizing the loss of visual quality.

Future Perspectives of Image Processing
The future of image processing holds immense potential as emerging technologies and advancements continue to push the boundaries of what can be achieved. Some exciting prospects include:
- Deep Learning in Image Processing: Deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have revolutionized image processing by achieving remarkable results in tasks like image recognition, segmentation, and generation.
- Real-Time Image Processing: The demand for real-time image processing is rapidly growing, particularly in fields such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality. Advancements in hardware and algorithms are making real-time processing more accessible and efficient.
- 3D Image Processing: With the proliferation of 3D imaging technologies, including depth cameras and LiDAR sensors, 3D image processing is gaining momentum. It presents exciting possibilities for applications such as 3D reconstruction, augmented reality, and virtual reality.
- Ethical Considerations: As image processing becomes increasingly pervasive, ethical considerations regarding privacy, bias, and data security become paramount. Addressing these concerns and establishing responsible practices for the ethical use of image processing technologies is crucial.
Conclusion
The landscape of visual information interaction has been transformed by image processing, catalyzing advancements across various industries and significantly enhancing our daily experiences. The future of image processing holds immense potential, driven by ongoing technological innovations and the emergence of novel techniques.
In realizing the full scope of image processing’s capabilities, it is crucial to employ its power responsibly and ethically. By doing so, we can harness its potential for the greater good of society. As we delve into the future, the prospects for image processing are indeed promising. Embracing these advancements can pave the way for a visually enriched and ethically conscious world.
For more detailed information on this topic, you can refer to our blog titled “How to Create a Consistent Design System for Your UI/UX Project.